On-page seo optimization techniques

On-page SEO optimization techniques is one of the most important processes you can use for achieving higher rankings in a search engine’s organic results and running successful SEO campaigns.
“Content is king” is an adage you may have heard a million times, but the scenario has changed: “ Relevant content is king” is the new mantra and is an apt motivator toward a streamlined UX. You should focus on user intent and user satisfaction rather than design sites for the search engines.
On-page optimization is related to factors controlled by you or your code that have an effect on your site’s rankings in search results.
6 On-page seo optimization techniques
To create an optimal experience, you need to focus on the following page-optimization factors:
Heading Tags (h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, and h6)
Heading tags are an important on-page factor. The <h1> (heading 1) tag is crucial and must be relevant to the topic discussed on the web page. It educates readers about the topic on that page. Instead of filling a page with clutter, it is a good practice to stick to a single topic; the heading 1 tag is imperative, because it indicates the page’s topic.
Use relevant words in the heading to help users and also spiders understand the page’s content. Google adheres to text semantics and emphasizes its use for better results.
Avoid skipping heading levels on a web page. <h1> should be followed by <h2> , which in turn may have a <h3> , and so on. You may have multiple <h2> tags or subsequent tags, if needed. Your web page must display a systematic pattern or consistency. If the formatting or styling of the headings is not to your liking, you can use CSS styling to alter it.
Include keywords, but do not repeat them in the heading. Keywords used at the beginning of a heading yield better results. Avoid spamming or using irrelevant words in headings, because doing so may have a negative effect.
Title Tag Optimization
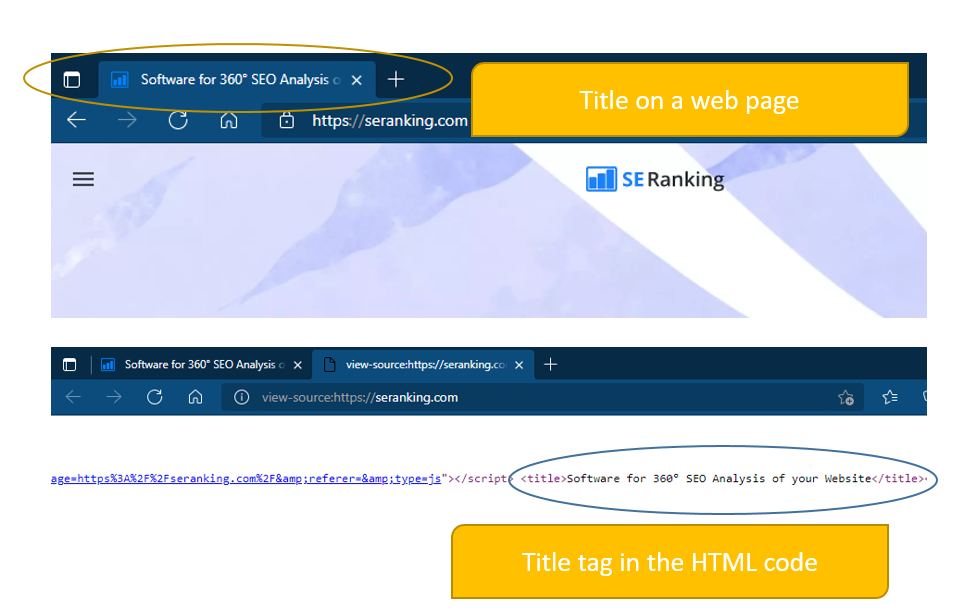
In a page’s HTML code, the <title> tag gives an indication of the page content. (You can find the words used between the <title> tags by viewing the page source in Firefox; the method varies depending on the browser.)
Next figure shows the location of a title on a web page as well as where it can be located in the code.
Search engines display the page title as the title of the search snippet link on SERPs.
However, the title of a search snippet may also depend on the search query.
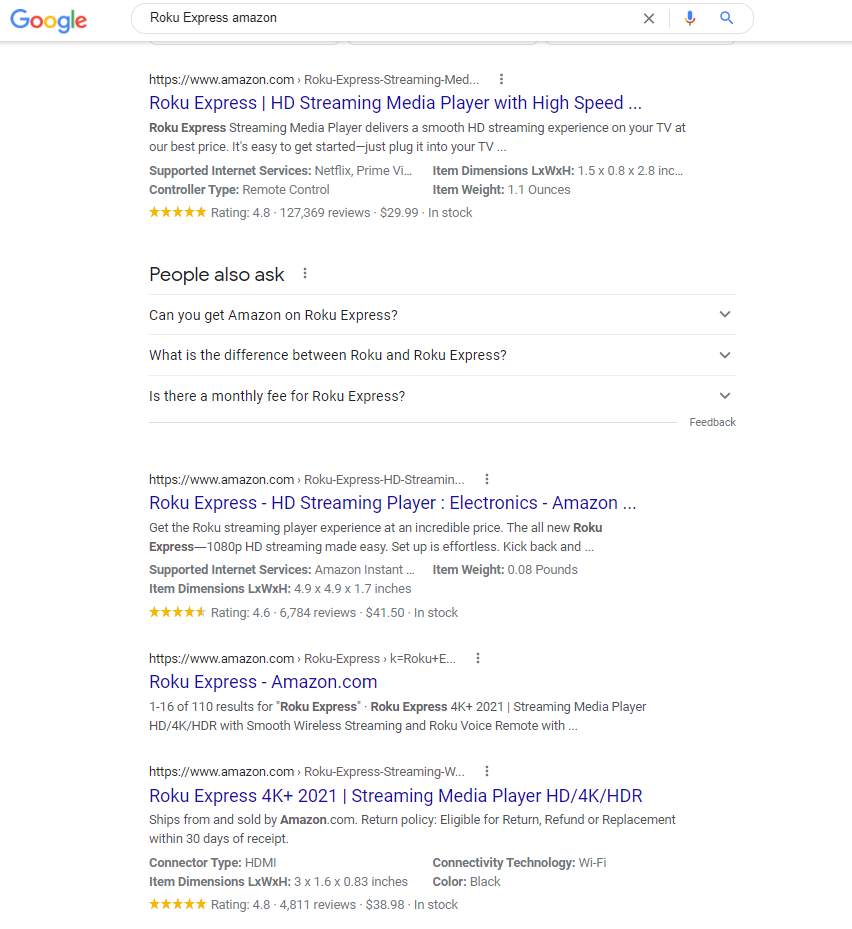
Next figure shows the search results for a query about a Roku Express amazon in Google Search in the browser.
This example uses Roku Express 4K+ amazon as the search query; therefore, in the highlighted box in the search results, you can see the website search snippet for that Roku on Amazon.
Now let’s change the search query to Roku Express 4K+ amazon. The results list the same website, but the title of the search snippet is different.
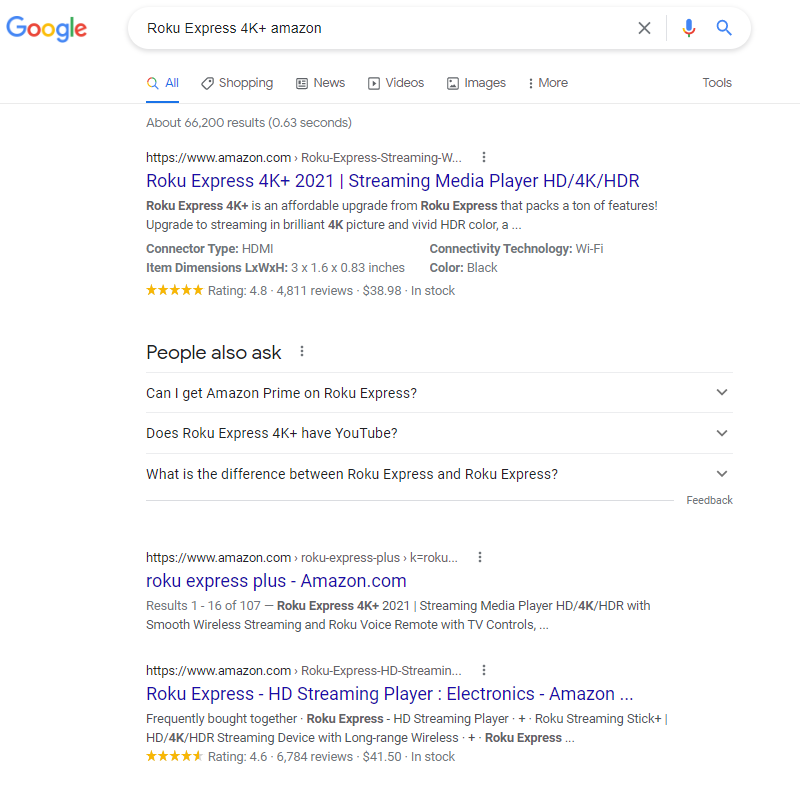
Over time, depending on the links and their age, a search snippet may change dynamically for the same result. Thus there is no fixed rule for how to create a page title.
The title may also vary depending on the platform—especially for responsive websites on small, medium, and large screens.
Also avoid using irrelevant phrases or a single keyword in the page title.
Your page title should educate users about the page content and thus must be relevant and related to the page content.
Single keywords face a lot of competition, because thousands of websites use the same keyword; it is better to use long-tail terms, which may be a mix of keywords and related phrases. Also keep in mind that each page on the website should have a unique title.
The best practice, according to SEO experts, is to use a phrase containing relevant words (say, 8–11 words) with at most 55–65 characters. This makes sense, because extremely long phrases will not work well on mobile devices where space is a constraint.
Titles must be precise and concise, and can use a mix of uppercase and lowercase characters.Avoid commonly used titles or duplicate content, because search engines display a preference for unique titles.
Google Search prefers function over form, so it is a best practice to use a simple, unique title rather than a sensational, irrelevant title. You should understand and consider user intent rather than looking at titles from a search engine point of view.
Meta Keywords and Meta Descriptions
Google confirmed that it doesn’t consider meta keywords and descriptions as ranking factors.
Nevertheless, meta keywords and meta descriptions are cached, so it would not be a best practice to ignore them. Although they are not consequential in determining search engine results, meta descriptions can be an excellent way of advertising; they may or may not be displayed in the search results.
Next figure provides an example of a meta description. It is a good practice to limit the meta description to 155–170 characters. It provides a preview of the content or information on that page and should contain the gist of the entire page. If the description is apt, informative, and meets the needs of the user, it may work like free advertising: the user may be compelled to click that site link to view the content.
The meta description must be unique for each page on a website, like the page title.
Avoid stuffing the description with keywords, and remove all special characters. Using multiple meta keywords can have a negative influence on search engines. The meta robots attribute is increasingly being used by web designers. It tells crawlers whether the page should be displayed in SERPs (index/noindex) or whether you should depend on the links on the page (follow/nofollow).
Engaging Content
Using meaningful and pertinent content in the body section of the site is vital. Relevant content is king. The content should not be irrelevant or stuffed with keywords—the search engines may penalize you for it. However, you can use keywords or close variations of them twice or three times on a page in a logical way.
The content should be informative and engage the user, encouraging them to return to check out the site regularly. It is a good practice to update the content (such as technology topics) at least every six months, because Google has a penchant for updated or fresh content. (News channel sites update their content on a daily basis. Here, we are referring to product pages or informative sites, and updating or adding content for a product or topic.)
Blogs must be updated on a regular basis. Use interactive media such as images, videos, and audio files on your web pages; they are intuitive and engage users, and may make the site more popular. Always spell-check and proofread your content, because incorrect grammar or spelling errors can reflect negatively on your site.
In addition to having meaningful content, quantity of content matters. You cannot use a keywords 3 times in 140 characters—that is keyword stuffing.
In-depth, detail oriented, relevant content helps you space out keywords evenly. It also helps users to understand the logic of the content, especially if the topic is informative and educates the user significantly.
However, do not use 2,000 words just to fill the page; low-quality content results in bad UX. Remember, less is more, because quality is more important than quantity—function over form.
Bounce rate reflects the number of users who visit a web page and then leave. It doesn’t matter how much time they spend on the page; it focuses on whether users leave the site after viewing just one page. Low-quality content results in higher bounce rates and will eventually affect the site’s visibility.
Do not copy content from another website or use boilerplate content. Google search engines have been known to penalize sites that use duplicate content. Focus on user satisfaction and not on fooling the search engines.
At times there are legitimate reasons for duplicate content: for example, an e-commerce site will have the same content on different pages with different URLs due to filters such as size, color, and price.
Some websites have the same content on different web pages with the prefixes HTTP and HTTPS ; although the rest of the URLs are the same, the prefixes mean they are treated as separate pages.
Sometimes the watered-down mobile version of a website has the same content as the desktop version, resulting in duplication. Localization may also be a factor: for example, www.google.com may appear as as www.google.es for Spain. The content may be the same, but the URLS are different. In such cases, search engines may not allocate as high a ranking, because two different URLs have the same or similar content.
You can resolve these issues by using either a canonical tag or a 301 direct. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect from one URL to another that helps users reach the new address. It can also be used for “404 Page not found” errors where content has been moved to a different web page.
A canonical tag is an alternative where you apply a rel=canonical attribute to tell search engines the original or preferred content and the URL to be indexed for display in SERPs.
For example, suppose these two websites have the same content:
http://example97653.com and http://example234.com/seo12345/56473 .
The first URL is the original, getting the maximum number of hits. You want this site address to be indexed. To implement the canonical tag, you go the HTML code for the second URL and, in the element, add the following:
You use the canonical attribute in the head element of the HTML markup for the URL containing the duplicate content and link it to the original or preferred URL.
Image Optimization and Interactive Media
Earlier SEO was text-based, but this has changed significantly. You should use interactive media such as audio, video, images, and infographics to connect with your users.
Use captions and alternate text for media, and build relevant content around these media. You can use a single key phrase in the alt text if it is relevant to that image.
You can interchange images based on the screen size, with heavy-duty images for desktop sites and lightweight images for mobile sites. Try to limit the image file size to less than 80–90 KB for optimal page-loading time. Use PNG or JPEG image formats wherever possible, because they are robust and have more visual properties.
Using thumbnails and different angles for a product can be very handy, especially on e-commerce sites.
Using videos explaining a product or marketing a certain entity is a good practice. Google owns YouTube, and it can be a game-changing means of branding your product. Infographics are an excellent way to provide information or create timelines with relevant content.
Outbound and Internal Links
Internal links are a key feature of SEO. These are links on web pages that point to another page in the site or domain.
SEO-related research suggests that no page on your website should be more than three clicks from the home page, meaning all pages should be easily accessible. You can use relevant anchor text to point to different pages on your site.
Breadcrumbs are an efficient way to provide site navigation using links. Having a good link structure makes it easy for search engines to crawl your entire website, and easy accessibility also leads to an awesome UX.
Outbound links point to another domain or site. They are a good feature for informative or niche topics. Sometimes a page includes jargon or topic-specific terms; instead of wasting time explaining supplementary information on the page, you can use URLs or anchor text as outbound links to locations that explain the information in depth.
SEO experts tend to doubt the content found on Wikipedia, but it is actually an excellent source of free, relevant, detail-oriented information.
For example, suppose you are explaining web servers, and you use the word server in your content. Instead of explaining what a server is, you can use the word as anchor text to link to a wiki site that explains the meaning and use of servers. Linking specific terms to wiki sites such as Wikipedia and Webopedia may boost your SEO process.
Not only is doing so relevant, but it also lends a certain amount of trust and credibility to your site.
You can use outbound links to social media sites or blogs to help reach out to a larger audience. Just be sure you do not link to spammy or illegal sites—doing so may negate your SEO efforts, because search engines will penalize your site. Also do not link to sites that are not relevant to the topic, because twoway linking or link farming can be detrimenta.
Si quieres conocer otros artículos parecidos a On-page seo optimization techniques puedes visitar la categoría SEO Foundations.
Leave a Reply